Mauritania: History, Slavery, and Desert Landscapes
Omar HassanExplore Mauritania's history, geography, and challenges, from slavery to desertification.
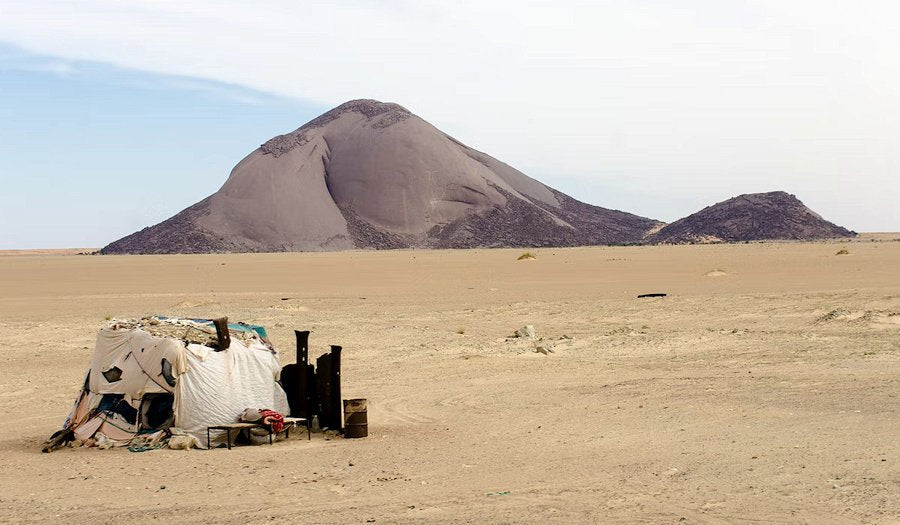

Mauritania, officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania, is a nation in Northwest Africa with a rich history and unique geographical challenges. It gained independence in 1960 but has faced political instability and environmental concerns.
Understanding Mauritania requires acknowledging its past, present conditions, and future prospects amidst a changing global landscape. This article delves into key aspects of Mauritania, providing insights into its culture, economy, and society..
Highlights
- Mauritania is largely desert, with 90% of its land in the Sahara.
- The country was the last to abolish slavery, only criminalizing it in 2007.
- Mauritania has significant natural gas reserves discovered in 2019.
Top 5 Key Insights
• Dominance of the Sahara: Approximately 90% of Mauritania is covered by the Sahara Desert, impacting agriculture and water resources. This geographical reality shapes the country's climate, lifestyle, and economic activities, with most of the population residing in the southern regions. Desertification remains a significant environmental challenge.
• Lingering Effects of Slavery: Mauritania was the last country to abolish slavery in 1981 and criminalize it in 2007. Despite these legal measures, slavery-like practices persist, particularly affecting the Haratin ethnic group. The government faces ongoing challenges in enforcing the abolition and addressing the deep-rooted social issues related to this historical practice.
• Economic Dependence on Natural Resources: Mauritania's economy relies heavily on agriculture, fishing, and mineral resources, especially iron ore. The discovery of oil in 2001 and large natural gas reserves in 2019 offer potential for economic diversification. However, sustainable management of these resources is crucial for long-term economic stability and development.
• Cultural Crossroads: Mauritania is culturally and politically part of the Arab world, with Arabic as the official language and Islam as the major religion. However, Mauritanian society is multiethnic, comprising Bidhan and Haratin groups, reflecting a blend of Arab-Berber cultures. This diversity enriches the country's cultural heritage but also presents challenges in fostering social cohesion.
• Historical Significance: In the Middle Ages, Mauritania was the cradle of the Almoravid dynasty, which played a significant role in spreading Islam across North Africa and into Spain. The country's name is derived from Mauretania, an ancient Berber kingdom. These historical connections highlight Mauritania's strategic importance throughout history.
Expert Insights
Ben Wilder, International Driving Authority: "Mauritania is predominantly just deserts. Approximately 90% of its land area falls within the Sahara Desert, making it one of the most arid countries in the world".
Afrikanza: "Mauritania was the last country to legally abolish slavery; it only became punishable as a criminal act in 2007. Slavery in Mauritania is deeply embedded".
Wrap Up
Mauritania's story is one of resilience amidst harsh environmental conditions and historical challenges. While the country grapples with issues like desertification and the legacy of slavery, it also possesses valuable natural resources and a rich cultural heritage.
Overcoming these challenges will require strategic planning, sustainable resource management, and continued efforts to promote social equality, paving the way for a more prosperous and equitable future.
Author
Omar Hassan - An experienced international affairs correspondent with a global perspective on major world events and diplomacy. He brings insightful commentary on global trends and international relations to Enlightnr.
More to Explore
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.